$89 New patient Exams & X-rays / $35 Emergency Visits
What to Do If a Root Canal Gets Infected?
Dealing with a root canal infection can be a daunting experience, often accompanied by significant discomfort. Knowing how to effectively manage this condition is crucial for alleviating symptoms and avoiding further dental complications. In this blog, we will discuss the causes, warning signs, and essential steps to take if you suspect a root canal infection.
Root canal infections occur when bacteria penetrate the innermost part of a tooth, causing inflammation and infection in the dental pulp. This often happens due to untreated cavities, dental injuries, or cracks in the tooth structure. As the infection worsens, symptoms such as intense tooth pain, heightened sensitivity to hot or cold, gum swelling, and even pus discharge may appear.
Recognizing these symptoms and taking swift action can prevent the infection from spreading and help maintain your overall oral health. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the best practices for managing an infected root canal and highlight when it’s time to seek professional dental care.
What You Must Know About Root Canal Infections
Being aware of the causes and early signs of a root canal infection is vital for timely treatment and effective management.
Common Causes of Root Canal Infections
- Untreated Cavities: Deep cavities can reach the dental pulp, leading to infection.
- Dental Trauma: Injuries or fractures can expose the pulp to bacteria, resulting in infection.
- Cracked Teeth: Cracks in the tooth allow bacteria to enter and infect the pulp.
- Repeated Dental Work: Multiple procedures on the same tooth can weaken it, increasing infection risk.
Symptoms of an Infected Root Canal
- Severe Tooth Pain: Persistent, throbbing pain, especially when chewing or applying pressure.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Gum Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling around the affected tooth, often with discomfort.
- Pus Drainage: Pus or discharge around the tooth, a clear sign of active infection.
Steps to Take When Dealing with a Root Canal Infection
If you suspect a root canal infection, it’s essential to act quickly to ease discomfort and seek appropriate care.
Home Remedies to Ease Discomfort
- Saltwater Rinse: Gargling with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can relieve pain.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the cheek can numb the area and reduce swelling.
- Soft Diet: Stick to soft foods and avoid anything hard or crunchy that could worsen the pain.
- Elevated Sleeping Position: Keeping your head elevated while sleeping can reduce swelling.
When to Seek Professional Help
Professional dental care is critical for effectively treating an infected root canal and avoiding serious complications.
Why Immediate Dental Care Is Crucial
- Prevents Infection Spread: Early treatment stops the infection from spreading to other teeth or the jawbone.
- Relieves Pain: Professional care provides relief from the intense pain associated with the infection.
- Preserve Tooth Health: Quick intervention can save the tooth, avoiding the need for extraction.
- Prevents Abscess Formation: Timely treatment can stop the formation of an abscess, a painful pus-filled sac.
Treatment Options for Infected Root Canals
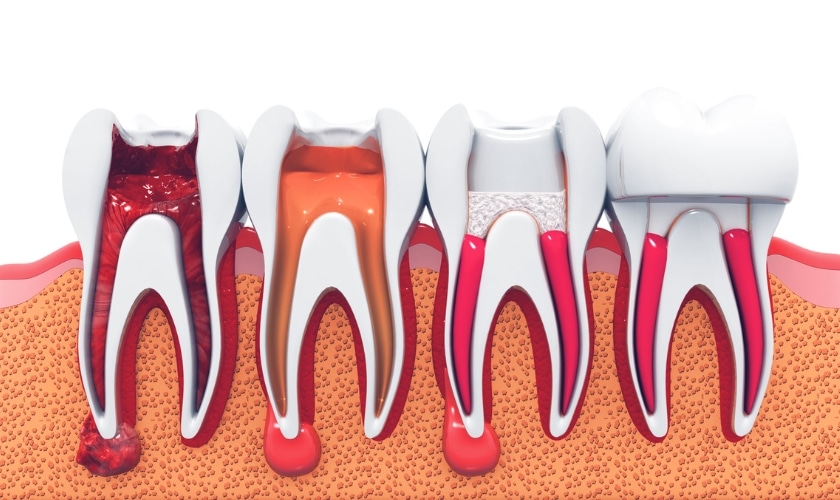
- Root Canal Therapy: This common treatment involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Endodontic Surgery: For severe cases or persistent infections, surgery may be needed to remove the infected tissue and restore oral health.
Complications and Risk Factors
Understanding the potential complications of untreated root canal infections and knowing the risk factors can help you maintain good oral health.
Complications of Untreated Infections
- Abscess Formation: Untreated infections can lead to abscesses, causing severe pain and swelling.
- Infection Spread: Without treatment, the infection can spread to other teeth, gums, or the jawbone.
- Tooth Loss: Severe infections can damage the tooth beyond repair, leading to extraction.
Risk Factors for Root Canal Infections
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to cavities and increase infection risk.
- Dental Trauma: Injuries to the teeth can expose the dental pulp to bacteria, causing infection.
- Untreated Cavities: Cavities left untreated can progress to pulp infections, requiring root canal treatment.
Tips for Preventing Root Canal Infections
Preventing root canal infections involves adopting healthy oral hygiene practices and protective measures to keep your teeth in optimal condition.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily and floss regularly to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule routine visits for professional cleanings and exams.
- Use Mouthguards: Protect your teeth during sports activities to prevent injuries.
- Avoid Hard Objects: Refrain from chewing on hard objects like ice or pens to prevent tooth damage.
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Reduce consumption of sugary snacks and beverages to prevent tooth decay.
Recognizing the signs of a root canal infection and acting quickly can help you preserve your oral health and prevent serious complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments empowers you to take control of your dental health. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking prompt dental care is key to preventing and managing root canal infections effectively.
